Gardens need special care during summer. Pollinator gardens are no exception.
Pollinator gardens play a crucial role in supporting bees, butterflies, and other pollinators. These small, hardworking creatures help our plants grow and produce food. Keeping your pollinator garden healthy ensures these vital insects thrive. But summer’s heat can be tough on your plants.
With the right tips, your garden can remain a vibrant, welcoming place for pollinators. This summer, make your garden a haven for these important visitors. Read on to discover 10 simple tips to keep your pollinator garden thriving in the hottest months. These tips will help you maintain a beautiful, buzzing garden all season long.
Choose Native Plants
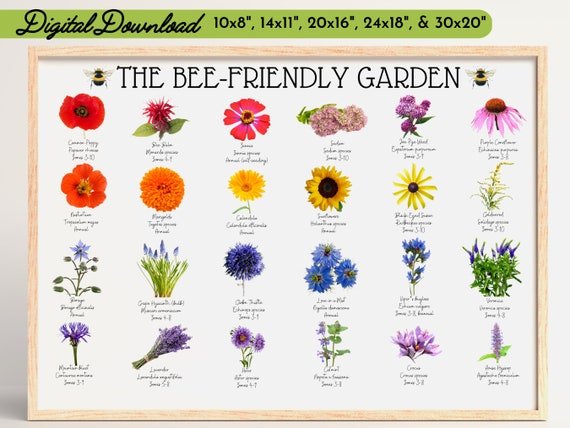
Creating a thriving pollinator garden is easier with native plants. These plants grow well in your local climate and soil. They also attract local pollinators like bees, butterflies, and birds. Let’s dive into why native species are important and which ones to choose.
Importance Of Native Species
Native plants are adapted to your region. They need less water and care. This makes them perfect for summer gardens. Native species also provide familiar food sources for local pollinators. They support the entire ecosystem.
Pollinators recognize these plants and visit them often. This increases pollination and helps your garden grow. Native plants also resist local pests and diseases. They reduce the need for chemical treatments.
Recommended Native Plants
Consider planting Milkweed. It is crucial for monarch butterflies. Bee Balm attracts hummingbirds and bees. Coneflowers offer vibrant colors and are hardy.
Black-eyed Susans are another great choice. They bloom all summer long. Asters provide late-season nectar for bees. Goldenrod supports pollinators into the fall.
Choose plants that suit your garden’s conditions. Match them with the light and soil type. This ensures they thrive and support pollinators.
Plan For Continuous Bloom
Keeping your pollinator garden blooming all summer requires careful planning. Ensuring a continuous bloom not only adds beauty but also supports pollinators. Different plants have different blooming times. By planning, you can have flowers throughout the season.
Seasonal Planting Guide
Consider the bloom times when selecting plants. Early bloomers can start the season. Mid-season and late bloomers can follow. This way, your garden stays vibrant. Plants like daffodils and tulips are great for spring. Summer can feature sunflowers and lavender. Fall brings chrysanthemums and asters. Mixing these plants ensures your garden blooms all summer.
Staggering Blooms
Staggering blooms means planting flowers that bloom at different times. This technique keeps your garden blooming. Plant early bloomers, mid-season bloomers, and late bloomers together. This way, as one flower fades, another takes its place. Your garden never looks dull. You can create a schedule. This helps in knowing when to plant each type. Staggering blooms also benefits pollinators. They have a steady food supply throughout the season.
Provide Water Sources
Pollinator gardens need water sources. These gardens help butterflies, bees, and other pollinators. They need water to thrive. By providing water, you attract more pollinators. This also keeps your garden healthy and vibrant.
Ideal Water Features
Birdbaths are a great choice. They are easy to maintain. You can also use shallow dishes. Fill them with fresh water daily. Add some rocks for the pollinators to rest on. This prevents drowning. Another option is a small fountain. Moving water stays cleaner longer. It also attracts pollinators with its sound.
Maintaining Water Sources
Keep water sources clean. Change the water every day. This prevents algae and mosquito growth. Scrub the containers weekly. Use a mild, eco-friendly soap. Rinse well to remove any residue. Check for leaks or damage regularly. Replace broken items to keep the area safe.
Use Organic Practices
Using organic practices in your pollinator garden creates a healthy environment. It ensures the safety of bees, butterflies, and other pollinators. Organic methods keep your garden thriving without harming the ecosystem.
Avoiding Pesticides
Pesticides can harm beneficial insects like bees. They can also damage the soil. Choose organic alternatives to keep your garden safe. Compost and natural fertilizers help nourish plants without chemicals. This leads to a healthier garden.
Natural Pest Control Methods
Use natural methods to manage pests. Introduce ladybugs and spiders to your garden. These insects eat harmful pests and protect your plants. You can also use neem oil or garlic spray. These natural solutions deter pests without chemicals.
Create Shelter
Creating shelter for pollinators is essential for a thriving garden. It provides a safe space for them to rest, reproduce, and escape from predators. Shelters help maintain a healthy ecosystem in your garden. Let’s explore the different types of shelter you can create.
Types Of Shelter
There are various shelters you can add to your garden. Each type serves a unique purpose and benefits different pollinators.
- Natural Shelters: Trees, shrubs, and grasses provide natural hiding spots.
- Artificial Shelters: Man-made structures like bee hotels and butterfly houses.
- Ground Shelters: Bare soil patches for ground-nesting bees.
Building Bee Hotels
Bee hotels are great for solitary bees. They provide a place for bees to lay eggs and protect larvae.
- Select Materials: Use untreated wood, bamboo, and paper tubes.
- Drill Holes: Create holes of different diameters. This attracts various bee species.
- Assemble: Bundle the materials together in a wooden box. Ensure the holes face outward.
- Place: Position the bee hotel in a sunny spot. It should be at least 3 feet off the ground.
Maintaining your bee hotel is important. Clean it yearly to prevent disease and parasites. By creating shelters, you provide a safe environment for pollinators. This helps your garden thrive.
Maintain Healthy Soil
Maintaining healthy soil is crucial for a thriving pollinator garden. Healthy soil supports plant growth, retains moisture, and provides essential nutrients. It also encourages beneficial microorganisms and insects. Let’s explore some ways to maintain healthy soil.
Composting Tips
Composting is a fantastic way to enrich your soil. Here are some tips:
- Use kitchen scraps: Vegetable peels, coffee grounds, and eggshells.
- Avoid meat and dairy: They attract pests.
- Balance greens and browns: Mix fresh, green materials with dry, brown ones.
- Turn the pile: Aerate your compost every few weeks for faster decomposition.
- Keep it moist: Water your compost to keep it damp, not soggy.
Soil Testing And Amendments
Testing your soil helps you understand its needs. Follow these steps:
- Collect samples: Take soil from various garden spots.
- Use a test kit: Analyze pH and nutrient levels.
- Amend accordingly: Add lime to raise pH or sulfur to lower it.
- Add organic matter: Use compost or manure to improve soil structure.
- Monitor regularly: Check soil health every season.
Healthy soil leads to healthy plants. Your pollinators will thank you!
Incorporate Variety
Incorporating variety into your pollinator garden is essential for its success. A diverse range of plants attracts a wide array of pollinators. This ensures your garden thrives throughout the summer. By choosing different types of plants, you provide food and shelter for many species. This helps create a balanced and vibrant ecosystem.
Diverse Plant Selection
Selecting a diverse range of plants is key. Include flowers, shrubs, and herbs. Different plants bloom at different times. This keeps pollinators coming to your garden all season long. Choose native plants as they are well-suited to the local climate. They also require less maintenance.
Mix perennials and annuals. Perennials come back year after year. Annuals add color and variety. Planting both ensures continuous blooms. This keeps pollinators fed and happy.
Benefits Of Plant Diversity
Plant diversity has many benefits. It attracts various pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and birds. Different pollinators prefer different plants. A diverse garden meets their needs. This increases pollination rates and plant health.
Diverse gardens are also more resilient. They are less likely to suffer from pests and diseases. Different plants support each other. Some repel pests, while others attract beneficial insects.
Lastly, a diverse garden is visually appealing. It offers a mix of colors, shapes, and textures. This makes your garden a beautiful and welcoming space.
Monitor And Record
To keep your pollinator garden thriving, constant monitoring is key. Recording observations helps you understand what works and what needs improvement. This practice provides valuable insights, allowing you to make informed decisions to benefit your garden and its visitors.
Keeping A Garden Journal
A garden journal is an essential tool for any gardener. Use it to note planting dates, bloom times, and weather conditions. This information helps track growth patterns and identify the best conditions for your plants.
You can use a simple notebook or a digital app to maintain your journal. The important thing is consistency. Write down observations daily or weekly, focusing on changes in plant health, flower production, and any pests.
Include sections for each plant species. Record the specific care they need. This will help you understand which plants thrive best in your garden’s unique conditions.
Tracking Pollinator Activity
Tracking pollinator activity is crucial. It helps gauge the success of your garden in attracting bees, butterflies, and other pollinators. Note the types and numbers of pollinators you observe.
Use a table to organize your observations:
| Date | Pollinator Type | Activity Observed | Plant Visited |
|---|---|---|---|
| June 1 | Bee | Collecting nectar | Lavender |
| June 2 | Butterfly | Resting | Sunflower |
Tracking these details helps you understand which plants attract the most pollinators. Adjust your planting strategy based on your findings to enhance your garden’s appeal.
You can also use photos to document pollinator visits. This visual record can be helpful for identifying different species and understanding their preferences.
By monitoring and recording your garden’s progress, you can ensure it remains a vibrant haven for pollinators all summer long.
Engage With The Community
Engaging with your community can significantly enhance your pollinator garden’s success. By connecting with others who share your passion, you can gain new insights, share resources, and create a network of support. In this section, we will explore two effective ways to engage with your community: joining garden clubs and participating in citizen science projects.
Joining Garden Clubs
Garden clubs are excellent platforms to connect with fellow gardeners. These clubs often organize events, workshops, and field trips, providing opportunities to learn and share knowledge. By being part of a garden club, you can:
- Exchange tips and techniques with other gardeners.
- Attend talks by experts in the field.
- Participate in group projects and community gardens.
- Access resources such as seeds, plants, and tools.
Most garden clubs also focus on specific themes, including pollinator gardens. This makes them an ideal space to discuss and learn about creating and maintaining a thriving pollinator-friendly environment. Find a local garden club and join their next meeting.
Participating In Citizen Science
Citizen science projects allow you to contribute to scientific research and conservation efforts. By participating, you can help scientists gather data on pollinator populations, plant health, and more. Some benefits of joining citizen science projects include:
- Gaining a deeper understanding of your local ecosystem.
- Helping to track and protect pollinator species.
- Receiving training on how to observe and record data effectively.
- Contributing to meaningful scientific research.
Many organizations run citizen science projects, such as the National Pollinator Garden Network and Xerces Society. Check their websites to find projects you can join. Your participation can make a significant difference in protecting pollinators and their habitats.
Prepare For Next Season
As summer winds down, it’s crucial to think ahead. Your pollinator garden needs care year-round. Preparing for next season ensures a thriving garden. Here’s how to get started.
Collecting Seeds
Begin by collecting seeds from your healthiest plants. This preserves the best traits. Let flowers dry on the plant. Then, carefully gather the seeds. Store them in a cool, dry place. Label each container clearly. This helps avoid confusion later.
Planning For Fall And Winter
Plan for fall and winter garden needs. Some plants benefit from fall planting. Research which ones work best in your area. Prepare your soil for the cooler months. Add compost or mulch to enrich it. Protect young plants with covers or straw. This shields them from frost.
Consider adding winter-blooming plants. They provide food for pollinators year-round. Examples include winter jasmine and snowdrops. These plants keep your garden active even in cold months.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should I Water My Pollinator Garden?
Water your pollinator garden deeply once a week. Ensure the soil stays moist, not soggy. Consistent watering supports healthy plants.
What Plants Attract The Most Pollinators?
Plants like lavender, coneflowers, and milkweed are excellent for attracting pollinators. Native plants are particularly effective.
How Can I Protect Pollinators From Pesticides?
Avoid using chemical pesticides in your garden. Opt for organic alternatives or natural pest control methods to protect pollinators.
Why Is Mulching Important For A Pollinator Garden?
Mulching helps retain soil moisture and regulate temperature. It also suppresses weeds, creating a healthier environment for pollinators.
Conclusion
Keep your pollinator garden thriving with these simple tips. Attract bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds by providing diverse flowers. Water regularly, but don’t overdo it. Mulch helps retain moisture and control weeds. Avoid pesticides; they harm pollinators. Plant native species for better adaptation.
Create shelter with bushes or trees. Add a shallow water source for hydration. Deadhead flowers to encourage new blooms. Rotate plants to maintain soil health. Enjoy watching your garden flourish with happy pollinators. A thriving garden benefits everyone. Happy gardening!